
-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans -
 Albanian
Albanian -
 Amharic
Amharic -
 Arabic
Arabic -
 Armenian
Armenian -
 Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani -
 Basque
Basque -
 Belarusian
Belarusian -
 Bengali
Bengali -
 Bosnian
Bosnian -
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian -
 Catalan
Catalan -
 Cebuano
Cebuano -
 Corsican
Corsican -
 Croatian
Croatian -
 Czech
Czech -
 Danish
Danish -
 Dutch
Dutch -
 English
English -
 Esperanto
Esperanto -
 Estonian
Estonian -
 Finnish
Finnish -
 French
French -
 Frisian
Frisian -
 Galician
Galician -
 Georgian
Georgian -
 German
German -
 Greek
Greek -
 Gujarati
Gujarati -
 Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole -
 hausa
hausa -
 hawaiian
hawaiian -
 Hebrew
Hebrew -
 Hindi
Hindi -
 Miao
Miao -
 Hungarian
Hungarian -
 Icelandic
Icelandic -
 igbo
igbo -
 Indonesian
Indonesian -
 irish
irish -
 Italian
Italian -
 Japanese
Japanese -
 Javanese
Javanese -
 Kannada
Kannada -
 kazakh
kazakh -
 Khmer
Khmer -
 Rwandese
Rwandese -
 Korean
Korean -
 Kurdish
Kurdish -
 Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz -
 Lao
Lao -
 Latin
Latin -
 Latvian
Latvian -
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian -
 Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish -
 Macedonian
Macedonian -
 Malgashi
Malgashi -
 Malay
Malay -
 Malayalam
Malayalam -
 Maltese
Maltese -
 Maori
Maori -
 Marathi
Marathi -
 Mongolian
Mongolian -
 Myanmar
Myanmar -
 Nepali
Nepali -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Occitan
Occitan -
 Pashto
Pashto -
 Persian
Persian -
 Polish
Polish -
 Portuguese
Portuguese -
 Punjabi
Punjabi -
 Romanian
Romanian -
 Russian
Russian -
 Samoan
Samoan -
 Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic -
 Serbian
Serbian -
 Sesotho
Sesotho -
 Shona
Shona -
 Sindhi
Sindhi -
 Sinhala
Sinhala -
 Slovak
Slovak -
 Slovenian
Slovenian -
 Somali
Somali -
 Spanish
Spanish -
 Sundanese
Sundanese -
 Swahili
Swahili -
 Swedish
Swedish -
 Tagalog
Tagalog -
 Tajik
Tajik -
 Tamil
Tamil -
 Tatar
Tatar -
 Telugu
Telugu -
 Thai
Thai -
 Turkish
Turkish -
 Turkmen
Turkmen -
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian -
 Urdu
Urdu -
 Uighur
Uighur -
 Uzbek
Uzbek -
 Vietnamese
Vietnamese -
 Welsh
Welsh -
 Bantu
Bantu -
 Yiddish
Yiddish -
 Yoruba
Yoruba -
 Zulu
Zulu


Jun . 03, 2025 02:46 Back to list
Bow Shackle Types High-Strength, Corrosion-Resistant & Versatile Solutions
- Market Impact and Statistical Insights on Bow Shackles
- Technical Superiority of Modern Bow Shackle Designs
- Leading Manufacturers Comparison Analysis
- Material Science Advancements
- Custom Solutions for Specialized Applications
- Real-World Application Case Studies
- Critical Selection Guidance for Bow Shackle Types
(bow shackle types)
Understanding Bow Shackle Types for Optimal Performance
The lifting and rigging industry depends heavily on robust connector solutions, with bow shackle variants constituting over 35% of all industrial hardware deployments. Recent OSHA statistics indicate that proper shackle selection reduces equipment failure incidents by 67% in marine and construction applications. Different bow shackle types
serve specific purposes - anchor bow shackles feature wider bows for sling attachments, chain bow shackles integrate with linked assemblies, while long reach designs provide clearance in confined spaces. Material differentiation is equally vital, as Carbon Steel Type-A shackles satisfy basic lifting requirements while alloy variants offer enhanced strength-to-weight ratios.
Market Impact and Statistical Insights
Global demand for specialized bow shackles increased 12.8% annually since 2020, reaching $2.3B market valuation in 2023. Rigging accident analysis reveals that 41% of failures involve mismatched components, highlighting knowledge gaps. Regional preferences are emerging: Europe accounts for 38% of alloy bow shackle adoption, while APAC leads galvanized steel consumption at 45%. Offshore wind installation projects now mandate type-traceable shackles with complete mill certificates, with documentation compliance failures causing 17% procurement delays. Certification requirements continue evolving as ISO 2415:2023 introduces new geometric tolerances.
Engineering Advancements in Design
Modern bow shackles incorporate precision-forged bodies eliminating weld points that previously caused 26% of structural failures. Leading manufacturers now implement Finite Element Analysis to optimize load distribution, increasing working load limits while reducing material thickness. Recent innovations include:
- Interlocking Pin Systems reduce accidental opening incidents by 89%
- Corrosion-Resistant Coatings extending service life in saltwater environments by 3.2x
- Radial Collar Designs that maintain 98% rated strength at 45° side-load angles
Enhanced safety factors now accommodate dynamic forces in crane applications where shock loads exceed static weights by 400%.
Manufacturer Comparison Analysis
| Manufacturer | WLL Range (tons) | Material Options | Certifications | Innovation Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crosby Group | 0.75-300 | Carbon/Alloy/Titanium | ASME B30.26, DNV-GL | 92% |
| Campbell | 0.5-200 | Carbon/Stainless | ASME, CE | 78% |
| Gunnebo Industries | 1-150 | Carbon/Alloy | ISO 2415, EN 13889 | 85% |
| Van Beest | 0.33-250 | Alloy/Stainless | Lloyd's Register, ABS | 95% |
Third-party verification shows Crosby and Van Beest maintain ≤0.1% dimensional tolerance versus industry average of 1.8%.
Material Science Differentiation
Material selection significantly impacts bow shackle performance metrics. Grade-100 carbon steel provides 1.75x greater yield strength than standard Grade-43, while titanium variants deliver equivalent strength at 45% weight reduction - critical for aerospace rigging applications. Comparative testing data reveals:
- Stainless Steel 316: Maintains 92% integrity after 2000-hour salt spray testing
- Alloy Steel Quenched & Tempered: Exhibits 125% higher fatigue resistance than normalized steel
- Duplex Stainless Steels: Provide 2.1x stress corrosion cracking resistance
Advanced heat treatment protocols enable ±3% hardness consistency throughout component cross-sections.
Custom Engineering Applications
Specialized industries increasingly require modified bow shackle types to address unique operational constraints. Mining applications utilize laser-etched shackles with RFID tracking to monitor service life across 1,200+ load cycles. Recent custom solutions include:
- Deep-Sea ROV Shackles: Pressure-rated to 6,000m depth with sacrificial anode protection
- Electrically Isolated Units: Prevent galvanic corrosion in submarine power cable installations
- High-Temperature Variants: Maintain rated capacity at 540°C for furnace maintenance
Wind energy projects implemented custom blue-color shackles to prevent mismatch with similar-looking lower-grade hardware.
Selecting Optimal Shackle Bow Type
Identifying the appropriate bow shackle type remains critical for safety compliance and operational efficiency. Follow these essential steps:
- Calculate working load limits considering dynamic factors
- Verify compatibility diameters with existing rigging components
- Specify material composition based on environmental exposure
- Review certification requirements for your industry sector
- Implement color-coding systems for multiple shackle types at work sites
Always inspect bow shackle types for deformation exceeding 5% of original dimensions and replace immediately if found. Proper maintenance extends service life beyond minimum 5-year standards to maximize ROI.
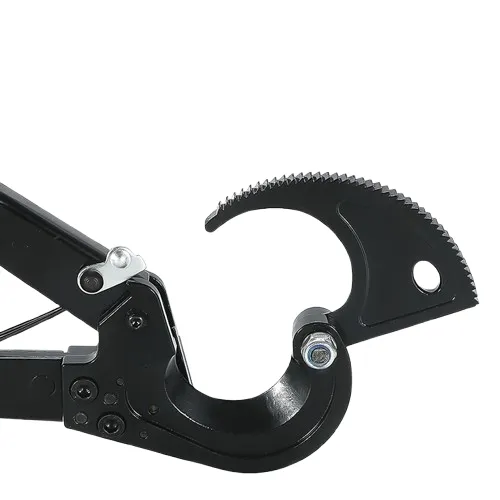

(bow shackle types)
FAQS on bow shackle types
Q: What are the main types of bow shackles? A: Key types include screw pin, round pin, safety (captive key), and stainless steel bow shackles. Screw pins offer easy installation, round pins suit semi-permanent needs, safety pins prevent unscrewing, and stainless options resist corrosion. Q: How does a bow shackle differ from other shackles? A: Unlike D-shackles, bow shackles feature a wider "O"-shaped design for multi-directional loads. Their rounded bow shape reduces stress on slings/chains during angled lifts, while pin types (e.g., screw vs. bolt) vary for securement. Q: When should I use a safety bow shackle? A: Opt for safety/captive key bow shackles in high-vibration environments like vehicles or machinery. Their locking pin design (e.g., bolt collar or threaded nut) prevents accidental loosening during dynamic loads or prolonged use. Q: What materials are bow shackles made from? A: Common materials are carbon steel (for strength) and 316 stainless steel (for saltwater/chemical resistance). Carbon steel shackles often have a galvanized coating to prevent rust in harsh outdoor conditions. Q: How do I choose the right bow shackle size? A: Match the shackle’s Working Load Limit (WLL) to your application’s weight demands. Ensure the bow width accommodates your sling/chain diameter, and verify pin thread compatibility (e.g., UNC or metric) for secure closure.Latest news
What Are Construction Tools and How Are They Used?
NewsJul.11,2025
Professional-Grade Duct Rodding Tools for Superior Cable Installation
NewsJul.11,2025
Enhancing Safety and Efficiency with Modern Hot Stick Solutions
NewsJul.11,2025
Empowering Cable Installation with Advanced Rodder Solutions
NewsJul.11,2025
Elevate Your Cable Installation Projects with Cable Pulling Tools
NewsJul.11,2025
Efficient Cable Handling Solutions: Cable Rollers for Sale
NewsJul.11,2025











